Advisor
Posted on 2022-01-25 By anuradha
Comparing SSD and NVMe - What`s main difference?
A lot has modified within the world of memory device within the past decade. Traditional spinning disk drives (HDD) are outperformed by really quick and very cost efficient Solid State Drives (SSD). And currently we've insanely quicker nonvolatile storage technology already offered for the consumers within the form of Non-Volatile Memory categorical (NVMe), that is manufactured in an exceedingly variety of various interfaces / form factors, including M.2.
SSDs are Solid State Drives that give a lot of quicker information transfer rates than magnetic disc drives. Before we answer the question, let’s discuss the SSD interface. An interface could be a slot or location on a motherboard where SSD could be hooked up to the system, either through a cable or directly via PCIe. Solid state drives are non-volatile storage devices that use flash-memory to store persistent data. They were invented before NVMe. NVMe is a software interface used to access the stored data in a computer. SSDs are a part of hardware while NVMe is a software that can be installed into the computer.
When it involves interfaces, they will be classified into 2 types:
Physical Interface: Those interfaces or form factors by which components connect to the system, or more precisely, the motherboard. For example, SATA and PCIe.
Logical Interface: Those architectural algorithms which operate inside those components to improve performance. For example, NVMe.
When we talk about a typical SSD, we refer to one having a SATA interface, that is the logical interface via that the SSD can connect with the motherboard through a SATA cable or PCIe . Thus, the question arises on what NVMe SSD signifies.
That is why, NVMe SSD refers to a solid-state drive which have an NVMe logical interface paired with an M.2 physical interface. NVMe is a Logical Architectural Algorithm which operates within the SSD and utilizes the M.2 interface to give the fastest data transfer rate possible.
Solid State Drives (SSD) have quickly become the quality and successor over traditional hard drives.SSD use NAND-Flash memory which is same that is used in USB drives and do not use any moving parts which allow it to perform much faster than a typical hard drive disk limited to 7200RPM. SSD’s usually cost the same as hard drives for typical storage sizes. But what makes it an easy choice is its significantly faster speeds. We would recommend using SSD for all server needs as it provides a perfect combination of cost and performance.
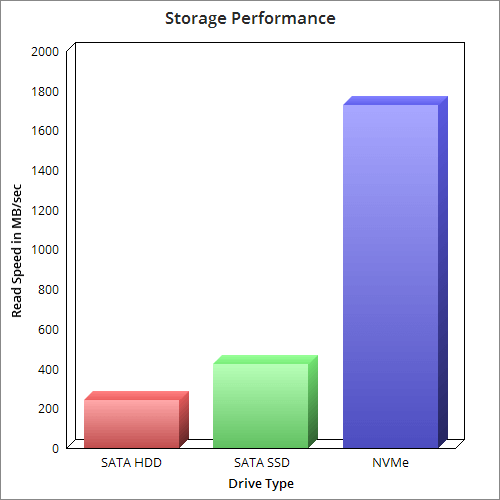
NVMe SSD drives are the most recent technology and supply the quickest transfer and I/O speeds. In fact, they’re nearabout 6x quicker than ancient SATA SSD. Hard Drives and traditional SSD use SATA III ports which produces maximum speed of 600MB/s and limit their speeds. Using this connection, most SSDs will provide read and write speeds of about 500 MB/s. For example, a 7200 RPM hard drive provides speed around 100MB/s depending on age, condition, and level of fragmentation. NVMe SSD on the other hand use multiple PCI-e lanes that allow it to manage throughput speeds as high as 3500MB/s. That’s 35x faster than hard drives and 7x faster than SATA SSDs.
Finally, NVMe drives within the consumer space are frequently provided in a form factor that removes the need for the drive’s oversized packaging and instead allows for the direct connection of a small and simple “M.2” circuit board to the motherboard, thus reducing the drive’s packaging, cabling, and physical connector costs.
